From the Data Analyst: How Sample Information Affects Limits and Analysis

Two questions our Data Analysis team often receives from fluid analysis customers are “What information is necessary to analyze our samples?” and “Why is this information so important?”
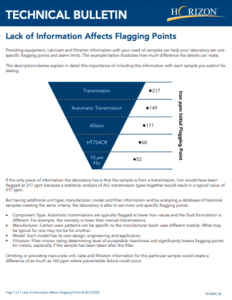
Whether your sample is defined as a grease, diesel fuel, lubricant or coolant, there are complex interpretation factors accounted for each test result of the respective application. Aside from establishing the appropriate testing slate applied to a fluid, test limits may also vary and be comprised of SAE, ISO, POLARIS Laboratories®, OEM, industry charter and/or fluid manufacturer standards. Due to these reasons, it is imperative to supply as much relevant equipment and fluid information as accessible to your laboratory when submitting the sample for testing.
Here are a few scenarios… Without fluid information, a laboratory may not be able to see abnormal fluctuations for additive content or viscosity. The fluid’s basicity may become essentially depleted prior to detection, or the acidic levels may be too high for neutralization efforts. Without the specific equipment model, a laboratory may have to rely on generic data points to extrapolate typical wear accumulation. These limits may be too aggressive or not aggressive enough for the type of equipment tested. These are all exact scenarios we have previously experienced with customers.
For example, we may factor the following information when establishing statistical trends for wear metal content, lubricant properties and interpreted recommendations:
- Equipment Type (e.g. engine)
- Specific Application (e.g. diesel)
- Equipment Manufacturer (e.g. Cummins)
- Equipment Model (e.g. ISX)
- Industry Type (e.g. logistics/transportation)
- Lubricant Manufacturer (e.g. Chevron)
- Lubricant Product (e.g. Delo 600 ADF)
- Lubricant Viscosity (e.g. 15W40)
- Filter Type (e.g. Full Flow)
- Filter Micron Rating (e.g. 10 micron)
- Sump Capacity (e.g. 14 gallon)
- Time on Lubricant (e.g. 13,598 miles)
- Time on Equipment (e.g. 124,600 miles)
While some equipment manufacturers have a ‘fixed’ wear limit table for operational guidelines, laboratories typically provide a more objective and literal statistical significance of normal wear accumulation. These statistics may reduce unnecessary calls for maintenance, which would otherwise lead to costly downtime or premature use of materials.
If you are unsure what information may be required to appropriately identify abnormal trends for your equipment samples, reach out to the laboratory for a list of the requisites and additional guidance. To receive an improved return on investment out of a lubricant, fuel, or coolant maintenance program, avoid delays or guesswork the laboratory may experience due to absent sample information.