Program Enrichment Review: It’s Not Just Data, It’s What You Do With It
Today’s fluid analysis capabilities offer a great deal more than just monitoring component health. With today’s technology, along with performing the proper tests, we can:
- Monitor the condition of the oil
- See if it is suitable for continued use
- Reduce the amount of used oil disposal
- Adjust maintenance intervals and strategies
- Adjust component replacement schedules
- Improve forecasting and budgeting
- Increase component life hours
With all of this in mind, it begs the question, how can we be sure to maximize the return on investment from fluid analysis? I believe the answer to this question is a Program Enrichment Review. Let’s take a look at some of the features/benefits of a Program Enrichment Review and what it can do with your data:
Pareto Principle
A “Pareto Principle” approach identifies the components that are contributing to the majority of high severity reports and helps identify corrective actions for your maintenance team. Let me share with you how POLARIS Laboratories® was able to use this principle to help a coal mining customer (see figure 1 below). Using Pareto Charts, POLARIS Laboratories® was able to determine that out of the 87 component types on file, only 11 component types were accounting for 80% of the high severity (3’s & 4’s) reports. By using additional Pareto Charts (not shown), POLARIS Laboratories® was able to identify the coal mine’s biggest problem was abrasive contaminants (ie. coal dust, dirt, etc.). By focusing the maintenance team’s efforts on these 11 component types, and using filter carts, kidney loop filtering, seal replacement, etc., the coal mine was able to address the abrasive contaminants issue and thereby realize a 6% reduction high severity reports over a 6 month period. The head of the maintenance team made the following statement about their fluid analysis program: “Guys, where can we spend a dollar today and get this kind of return on investment when it comes to protecting our equipment and extending its life cycle?”
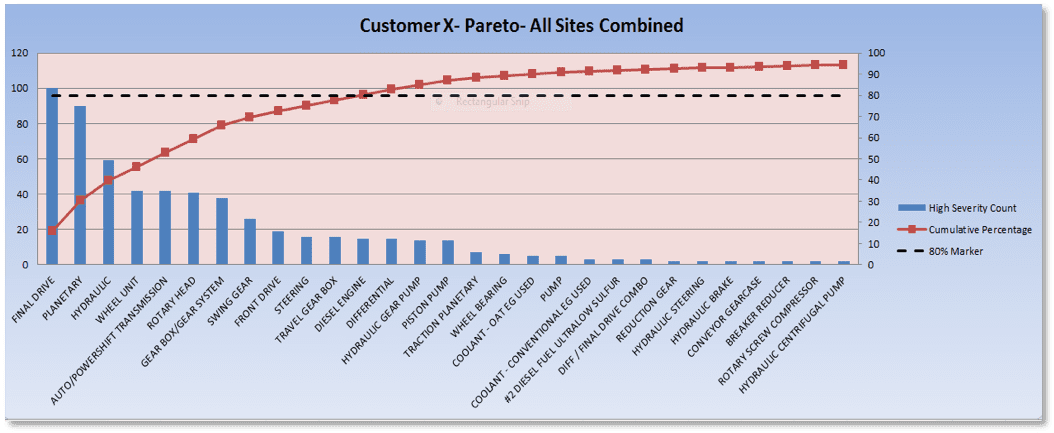
Figure 1
Typical Data Shared in a Program Enrichment Review
- Sample volume (i.e. total number of samples submitted per quarter)
- High severity reports (severity 3’s & 4’s / scale of 0-4) by region, location, asset, etc.
- Identify issues via Pareto charts (i.e. 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes)
- Scatter plots – help determine optimum drain intervals via key performance indicators (e.g. viscosity, acid number, base number, oxidation, fuel dilution, soot loading, etc.)
- HORIZON® web-based management reports (e.g. Problem Summary Report, Severity Summary Report, Data Analysis Report, Action Taken Summary Report – ROI, etc.)
- Scorecards (i.e. Component Compliance, Sampling Frequency Compliance, High Severity %, Shipping Time, etc.)
- Technical Business Consultant’s subject matter expertise (i.e. observations & recommendations)
Quarterly Program Enrichment Reviews
Delivering the Program Enrichment Review via a quarterly virtual meeting with the customer’s “Program Champion” and maintenance team will serve as a venue to share both challenges and best practices associated with their fluid analysis program and maintenance “best practices”.
It’s Not Just Data, It’s What You Do With It!
Maximize asset reliability and regain control of your production schedules with an effective fluid analysis program by POLARIS Laboratories® . . . it costs so little to protect so much.
Proven Impact. Proven Uptime. Proven Savings.
Let us prove it to you.






 Oil Analysis: The First Question
Oil Analysis: The First Question


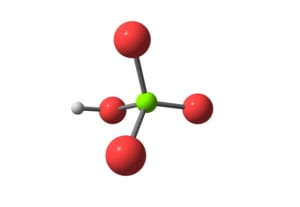
 Background on Base Number Testing
Background on Base Number Testing